The oil crisis of 1973 was a jarring reality for many American motorists as fuel became more expensive than it used to be. The only way out of this quandary was to use automobiles that consume less fuel without compromising power.
By the time another oil crisis came on the scene within that decade, i.e., 1979, many motorists were ready. This is where the Ford AOD transmission came into the picture.
A Brief History of The AOD Transmission
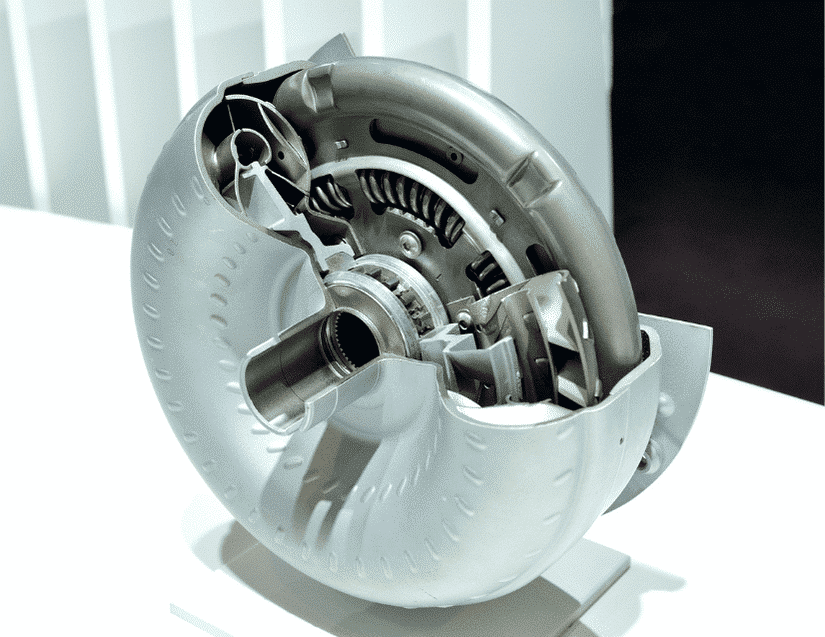
Ford introduced the automatic overdrive (AOD) in 1980, and it was the first domestic AOD transmission. Chrysler and General Motors soon followed suit. General Motors developed the 200 into a 200-4R with overdrive while Chrysler added more overdrive units to the existing 3-speed automatics: the 904 and 727. General Motors derived the all-new 700-R4 purpose-built AOD from the 200-4R.
The AOD may seem intimidating when placed with older FMX 3-speed, C4, and C6 automatics. The only difference is the direct overdrive lockup – to do away with wasteful slippage – and add-on hydro-mechanicals. The automatic overdrive came in a fresh-cast aluminum case with an overdrive unit as well as a trustworthy planetary gearset.
Ford’s all-new automatic overdrive is in full-size Mercurys, Fords, and Lincolns as a fresh design. However, it notably incorporated the existing tried-and-tested Ravigneaux geartrain components, conveniently borrowed from the BorgWarner FMX parts bin, i.e., the older and time-proven FX, MX, and FMX transmission family. The AOD is constructed mainly for small engine blocks.
The automatic overdrive is highly dependable, thanks majorly to the use of numerous time-proven components. It took several years before Ford could dial in the automatic overdrive as a pretty solid performer. But this only occurred with the assistance of off-road and aftermarket racers.
The Challenges with the Ford AOD Transmission
The Ford automatic overdrive was said to have durability issues, especially within the clunky overdrive unit known for its constant failure. The transmission’s third gear lacks clutches and additional steel, while its input shaft snaps easily when subjected to too much power.
The shift pattern is also a pain in the neck as it takes a bit to get used to if you want to shift to second gear. Moreover, if you shift into overdrive at full throttle, it wastes the clutch pack completely.
Even the stock cooler leaves a lot to be desired by racing enthusiasts who would love to wring lots of power out of their automobile.
However, the arrival of the 1993 Lincoln Mark VIII AODE (AOD Electronic) Control/4R70W’s wider band and overdrive drum solved this problematic issue.
The 3 Types of Ford AOD Transmissions Identification
The following are the 3 types of upgraded, finely tuned Ford automatic overdrive transmissions and their different price points:
- Ford AOD Performance Transmission (Level 2): $3,995.00
- Ford AOD Performance Transmission (Level 3): $4,995.00
- Ford AOD Performance Transmission (Level 4): $5,495.00
Each of these automatic overdrive transmissions is custom built from start to finish with the primary goal of making the Ford AOD transmission much better than it was.
For instance, the Ford AOD transmission (Level 4) is an extensive block-compatible gear system that is available along with a master overhaul kit. It also has the following features:
- A brand-new reverse band
- A high-capacity 3-plate intermediate clutch
- A 30,000 GVW cooler
- A carbon fiber overdrive band
- An updated overdrive servo pins and piston, etc.
This includes a much-wider reverse drum complete with a mechanical diode. On the whole, that is up to 700 horsepower with approximately 600 ft./lbs. torque. If there is room for additional modifications, you can talk to a professional or an experienced/certified technician or mechanic.
They are retrofit transmissions carefully and expertly remade with aftermarket parts to fit any performance enthusiast’s needs.
These Ford AOD transmissions come fully equipped with up to 20,000 GVW coolers, as well as several customizations geared towards high-performance driving.
Each Ford AOD transmission undergoes rigorous testing and is tested with a converter for the equivalent of up to 100 miles, just to ensure ideal operating conditions.
Fuel efficiency and performance make these Ford AOD transmissions sought-after as they are essentially horsepower transferring systems.
All Ford AOD transmission identification share similar gear ratios:
- First gear: 2.40:1
- Second gear: 1.47:1
- Third gear: 1:1
- Fourth gear: 0.67:1
Successors of the Ford AOD Transmission
The successors to the Ford automatic transmission are the electronically-controlled AODE and 4R7XX transmissions. Circuitry and computer parts play significant roles in the overall functions of these exceptional transmissions. This makes them markedly different from the mechanically-regulated automatic overdrive and old-school technology.
The manual shift mechanism of the AODE/4R70W transmissions is basically the same as the Ford AOD, except that it has no neutral safety/linear backup switch. Instead, this specific function is right outside the case.
This large, heavy electro-magnet component is the pressure control solenoid that pulses in order to control system pressure. If this component malfunctions, you will experience severe transmission damage.
The valve body of the AODE/4R70W is very much different from – and not interchangeable – with the original AOD. It lacks the throttle valve that comes with the AOD.
The shift-points and system pressure programming are not mechanically modulated but computer-controlled. The manual shifter valve comes with a bolt-on detent to lock shift positions.
The AODE initially came with a raw wiring harness that connects the multiplex system plug to the converter lockup solenoid and shift control solenoids.
The AODE and 4R70W transmissions come with a press-in filter that requires no installation and removal tools. You must take extra care in order to ensure the filter and rubber seal are highly secure before buttoning up. Do not reuse a filter.
You can find Ford casting numbers on all AODE, 4R70W, and even 4R75 castings. These numbers are crucial and play a significant role in revealing the type of transmission you have as well as which parts should be used.
Conclusion
There’s much more to your vehicle than transportation, and that is pushing machinery to its very brink and wringing maximum potential out of a custom-built power generator.
This is why you need nothing else but the custom Ford AOD performance transmissions explicitly tuned to keep you fully satisfied. Each Ford automatic overdrive transmission build is fine-tuned to make the most of the old AOD and bring it into the modern era of remarkable performance.