- Product
- Qty in Cart
- Quantity
- Price
- Subtotal
-
 Gearstar Performance Transmissions
Gearstar Performance TransmissionsChevrolet 700R4 Performance Transmissions 4×4 – Level 4
$5,495.00 -


-


-


-

-


-


-


-


-

-

-

 Gearstar Performance Transmissions
Gearstar Performance TransmissionsChevrolet Supermatic 4L85E Performance Transmission 2wd - Level 5 Pro Series
$19,995.00 -

 Gearstar Performance Transmissions
Gearstar Performance TransmissionsChevrolet Supermatic 4L85E Performance Transmission 2wd - Level 4
$9,495.00 -

 Gearstar Performance Transmissions
Gearstar Performance TransmissionsChevrolet Supermatic 4L85E Performance Transmission 4x4 - Pro Series
$14,445.00 -

 Gearstar Performance Transmissions
Gearstar Performance TransmissionsChevrolet Supermatic 4L85E Performance Transmission 4x4 - Level 4
$9,495.00 -

 Gearstar Performance Transmissions
Gearstar Performance TransmissionsChevrolet Supermatic 4L85E Performance Transmission 2wd - Level 3
$8,495.00 -
 Gearstar Performance Transmissions
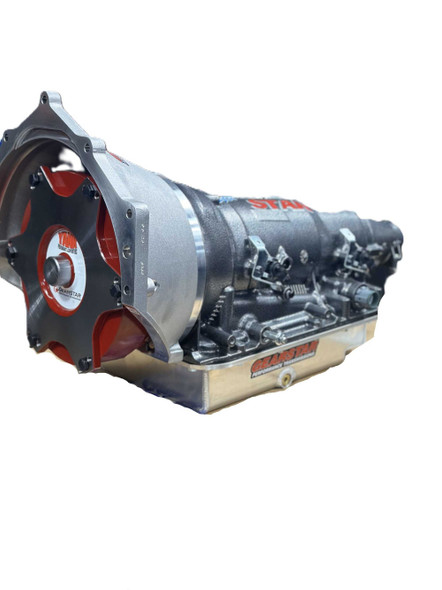
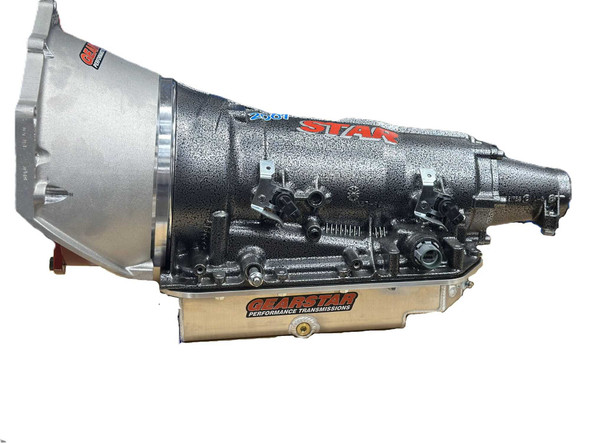
Gearstar Performance TransmissionsChevrolet 4L80E Performance Transmission 2wd - Level 5 Pro Series
$9,495.00 -


-

-

-
 Gearstar Performance Transmissions
Gearstar Performance TransmissionsChevrolet 4L80E Performance Transmissions 2wd - Level 2
$4,495.00 -


-


-


About Transmissions
Every transmission is handled by one technician from start to finish.
Each performance transmission is different and each customer has different needs. Allowing a single builder to craft your transmission means that he is intimately involved with both the transmission and the project. He has your requirements in mind at every point in the process.

Choose Your High-Performance Transmissions
At Gearstar Transmissions, we specialize in crafting high-performance automatic and manual transmissions for enthusiasts who demand the best.
The evolution and technical characteristics of automatic transmission systems have been remarkable, with General Motors introducing major models that have set industry standards. These systems have advanced significantly over the decades, utilizing a torque converter to facilitate gear changes without the need for a clutch.
Whether you are looking for a Ford performance transmission, a GM performance transmission, or a Mopar performance transmission – we’ve got you covered.
Every Transmission Assembly is Handled by One Technician from Start to Finish
When you trust Gearstar with your transmission, you’re not just getting a product—you’re getting a personalized experience. Each performance transmission is built by a single master technician who oversees your project from beginning to end. This ensures that every detail is tailored to your specific needs and vehicle requirements.
Using high-quality components, including valve bodies, ensures the best performance and reliability of your transmission system.
Having one technician dedicated to your build guarantees consistency, quality, and a deep understanding of your project. Your transmission is treated like it’s our own, with care and precision at every step, giving you peace of mind knowing your vehicle is in good hands.
We Only Build High-Performance Automatic and Manual Transmissions
At Gearstar, we live and breathe performance. We’re not here to rebuild everyday commuter vehicles—we’re here to power the cars that ignite your passion. Whether you’re driving a Ford, GM, or Mopar, we specialize in creating transmissions that deliver unmatched performance and reliability.
For Ford enthusiasts, we build transmissions that handle the power and performance of Mustangs, F-150s, and other iconic models. GM fans can trust us to deliver transmissions perfect for Camaros, Corvettes, and Chevy trucks. Turbo-Hydramatic models were initially identified by letters followed by a series or version number, but in 1987, GM transitioned to a simpler naming scheme that included a numerical designation indicating the specific model.
Gearstar builds automatic transmissions for Chevrolet vehicles, highlighting models like Camaros and Corvettes. And for Mopar lovers, we design transmissions that bring out the best in Challengers, Chargers, and other Mopar muscle cars.
We understand how much your car means to you, and we treat every build with the respect and attention it deserves.
Types of Transmissions
Automatic Transmissions
Automatic transmissions are designed to automatically change gears without the need for driver input. They use a complex system of sensors, hydraulic pumps, and gearsets to adjust the gear ratio and provide smooth acceleration. Automatic transmissions are popular in modern vehicles due to their ease of use and convenience. They are particularly well-suited for city driving and heavy traffic conditions.
Manual Transmissions
Manual transmissions, on the other hand, require the driver to manually change gears using a clutch pedal and gearshift. They offer more control over the vehicle and are often preferred by driving enthusiasts. Manual transmissions are typically more fuel-efficient and cost-effective than automatic transmissions, but they require more driver input and can be more challenging to use in heavy traffic.
The Best Transmission Parts Make the Best Transmissions
Quality starts with the components we use. At Gearstar, we source only the top US-made parts for our transmissions. From gears and clutches to seals and bearings, every part is selected for its durability and performance. Using genuine transmission assemblies ensures compatibility and optimal performance for various vehicle models.
We don’t cut corners. Our commitment to quality ensures that your transmission is built to last, even under the most demanding conditions. The torque converter plays a crucial role in automatic transmissions by allowing smooth gear changes without the need for clutch engagement.
If you’re looking for specific components for your build, we also offer a wide selection of premium transmission parts to help you customize your transmission to your exact specifications.
Types of Transmissions
Automatic Transmissions
Automatic transmissions are designed to automatically change gears without the need for driver input. They use a complex system of sensors, hydraulic pumps, and gearsets to adjust the gear ratio and provide smooth acceleration. Automatic transmissions are popular in modern vehicles due to their ease of use and convenience. They are particularly well-suited for city driving and heavy traffic conditions.
Manual Transmissions
Manual transmissions, on the other hand, require the driver to manually change gears using a clutch pedal and gearshift. They offer more control over the vehicle and are often preferred by driving enthusiasts. Manual transmissions are typically more fuel-efficient and cost-effective than automatic transmissions, but they require more driver input and can be more challenging to use in heavy traffic.
The Best Transmission Parts Make the Best Transmissions
Quality starts with the components we use. At Gearstar, we source only the top US-made parts for our transmissions. From gears and clutches to seals and bearings, every part is selected for its durability and performance. Using genuine transmission assemblies ensures compatibility and optimal performance for various vehicle models.
We don’t cut corners. Our commitment to quality ensures that your transmission is built to last, even under the most demanding conditions. The torque converter plays a crucial role in automatic transmissions by allowing smooth gear changes without the need for clutch engagement.
If you’re looking for specific components for your build, we also offer a wide selection of premium transmission parts to help you customize your transmission to your exact specifications.
Happy Builders Produce Better Builds
Our master builders are the heart of Gearstar. Each builder is handpicked for their expertise, skill, and passion for performance. We believe that happy builders produce the best work, which is why we provide them with the time, resources, and respect they need to excel.
Our builders are more than technicians, they’re enthusiasts who understand what it takes to create a transmission that performs. They ensure the transmission system works seamlessly with the engine for optimal performance.
Every transmission undergoes rigorous testing to ensure it meets our high standards before it reaches you, so you can trust that your build is in the best hands.
When it comes to your transmission, our builders are given the time and resources they need to do it right the first time.
Why Choose Gearstar Transmissions?
When it comes to high-performance transmissions, Gearstar stands out for several reasons. First, every transmission is built by a single master technician with years of experience, ensuring consistency and quality.
Second, we use only the best US-made components for durability and performance. Third, from start to finish, your build is tailored to your needs, providing a personalized experience.
Fourth, we offer a wide selection of transmissions and parts, whether you need a Ford transmission, GM transmission, Mopar transmission, or transmission parts.
Additionally, the historical development of automatic transmissions by General Motors, starting from the late 1930s through the 1950s, has significantly impacted the industry, showcasing the evolution and innovation in transmission systems.
Finally, we’re passionate about helping you achieve the performance you deserve, and your satisfaction is our top priority.
Need help choosing?
Ready to take your vehicle to the next level? Browse our selection of high-performance transmissions and parts. We offer Ford transmissions perfect for Mustangs, F-150s, and more.
Our GM transmissions are ideal for Camaros, Corvettes, and Chevy trucks, featuring world-class quality GM Genuine Parts engineered to meet high standards.
Choosing the right transmission can be overwhelming, but we’re here to help. Whether you’re upgrading your Ford, GM, or Mopar, our experts are ready to guide you through the process.
Answer some questions and we will be able to determine what the best transmission replacement would be. You can also contact our sales line at 330-434-5216. We look forward to hearing from you.



